Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Seno, Yasuhiro*; Noguchi, Akira*; Nakayama, Masashi; Sugita, Yutaka; Suto, Shunkichi; Tanai, Kenji; Fujita, Tomoo; Sato, Haruo*
JAEA-Technology 2016-011, 20 Pages, 2016/07
Cementitious materials are expected to be used for the construction of an underground repository for the geological disposal of radioactive wastes. Ordinary Portland Cement(OPC) would conventionally be used in the fields of civil engineering and architecture, however, OPC has the potential to generate a highly alkaline plume (pH 12.5), which will likely degrade the performance of other barriers in the repository such as the bentonite buffer and/or host rock. Low alkaline cementitious materials are therefore being developed that will mitigate the generation of a highly alkaline plume. JAEA has developed a High-volume Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) as a candidate low alkaline cementitious material. The workability of the HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by conducting In-situ full scale construction tests in the Horonobe underground research laboratory. This report summarizes the results of immersion tests to assess the long-term pH behavior of hardened HFSC cement pastes made with mix designs that are expected to be able to be used in the construction of an underground repository in Japan.
12.5), which will likely degrade the performance of other barriers in the repository such as the bentonite buffer and/or host rock. Low alkaline cementitious materials are therefore being developed that will mitigate the generation of a highly alkaline plume. JAEA has developed a High-volume Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) as a candidate low alkaline cementitious material. The workability of the HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by conducting In-situ full scale construction tests in the Horonobe underground research laboratory. This report summarizes the results of immersion tests to assess the long-term pH behavior of hardened HFSC cement pastes made with mix designs that are expected to be able to be used in the construction of an underground repository in Japan.
*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2001-007, 56 Pages, 2002/01
In the geological disposal concept of radioactive wastes, a kind of clay with sorption ability and low permeability, called bentonite, is envisaged as an engineered barrier system in the geological repository. Also, the cemetitious material is envisaged as the backfill material in the vaults and the structure material of the vaults. The groundwater in contact with the cementitious material will promote hyperalkaline conditions in the repository environment and these conditions will affect the performance of the bentonite. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the interaction between the cementitious material and the bentonite for the evaluation of long term stability of the disposal system. In this study, for the identification and the investigation of the secondary minerals, the batch immersion experiments of the powder bentonite were carried out using synthetic cement leachates (pH=7, 12.5, 14) at 200 C. As the results, it was confirmed that Na as exchangeable cations in the bentonite can exchange relatively easily with Ca in the solution from the experiment results. And the ratio of cation exchange was estimated to be about 25% based on the amount of exchangeable cations Ca
C. As the results, it was confirmed that Na as exchangeable cations in the bentonite can exchange relatively easily with Ca in the solution from the experiment results. And the ratio of cation exchange was estimated to be about 25% based on the amount of exchangeable cations Ca between layers. Furthermore, it was concretely shown that the generation of analcime might be affected by the Na concentration from results of the solution analyses and a stability analysis of analcime using the chemical equilibrium model, in addition to the pH in the solution.
between layers. Furthermore, it was concretely shown that the generation of analcime might be affected by the Na concentration from results of the solution analyses and a stability analysis of analcime using the chemical equilibrium model, in addition to the pH in the solution.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Kawasaki, Manabu*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*
JNC TN8400 2001-011, 62 Pages, 2001/03
The corrosion of metallic materials used in natural environment are sometimes affected by microbial action. It is apprehended that microorganism living in deep underground or brought from ground surface during excavation makes an impact on overpack material for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) is known to be one of the most representative microorganism which affects the corrosion of metals. In this study, the behavior of growth of SRB was investigated at first under the presence of bentonite as a main component of buffer material which encloses the overpack. The results of the tests showed that the population of SRB after the culture in synthetic sea water mixed with bentonite decreased with increasing the ratio of bentonite/solution. SRB was hardly grown in medium whose bentonite/solution ratio exceeded 1000g/l. As a conservative case, the effects of sulfide on the corrosion of overpack materials were also studied assuming high activity of SRB. Carbon steel, copper and titanium specimens were immersed in synthetic sea water purging 0.1MPa H S gas and the corrosion behavior was compared with the results in N
S gas and the corrosion behavior was compared with the results in N gas purging environment. Obvious effect of sulfide on the corrosion of carbon steel was not observed, but the corrosion rates of copper specimens were accelerated several hundred times by purging H
gas purging environment. Obvious effect of sulfide on the corrosion of carbon steel was not observed, but the corrosion rates of copper specimens were accelerated several hundred times by purging H S gas. The absorption of hydrogen into titanium specimens was not affected by purging H
S gas. The absorption of hydrogen into titanium specimens was not affected by purging H S gas, but the difference of hydrogen absorption between pure titanium and titanium alloy containing 0.06%-Pd was observed.
S gas, but the difference of hydrogen absorption between pure titanium and titanium alloy containing 0.06%-Pd was observed.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Taniguchi, Naoki; Honda, Akira
JNC TN7430 2000-002, 25 Pages, 2001/01
The burial tests of mild steel and pure titanium were performed in a gallery at Tono mine to assess the corrosion resistance of these materials under goundwater environment. Specimens were placed in the container and immersed into groundwater. After the immersion period, the apperance of the surface of these specimens were observed. The corrosion product of mild steel specimen was analysed by various methods. The average corrosion rate of mild steel for 10 years was assessed by the measurement of the weight loss of carbon steel specimen. The results of the test were summerised as follows : (1)The average corrosion rate of mild steel for 10 years was assessed to be 4.36  10
10 mm/y by the weight loss of the specimen. (2)The corrosion product consists of outer porous substance and inner tight corrosion product film. The former contains ferric oxide such as goethite and the latter contains ferrous oxide such as magnetite. (3)The evidence of the initiation of localised corrosion was not observed on the titanium specimens.
mm/y by the weight loss of the specimen. (2)The corrosion product consists of outer porous substance and inner tight corrosion product film. The former contains ferric oxide such as goethite and the latter contains ferrous oxide such as magnetite. (3)The evidence of the initiation of localised corrosion was not observed on the titanium specimens.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Aoki, Rieko*; Hirose, Ikuro
JNC TN7430 2000-001, 47 Pages, 2000/12
Long-term immersion tests of glass material at ambient temperature (about 18  C) for 10 years were performed in a gallery at the Tono mine in Japan, in order to assess durability of glass matelial contacted with natural groundwater. The gallery was constructed at a depth of 130 m below ground surface in the Toki Granite. Monolithic glass blocks with dimensions of 10
C) for 10 years were performed in a gallery at the Tono mine in Japan, in order to assess durability of glass matelial contacted with natural groundwater. The gallery was constructed at a depth of 130 m below ground surface in the Toki Granite. Monolithic glass blocks with dimensions of 10  10
10  10 mm (cubic type) and of 25 mm in diameter and 8 mm in thickness (disk type: The wall of sample was covered by stainless steel of 1 mm thick.) were used for the tests. Both type of samples with and without clay were put in Teflon vessels, which have small holes on the wall, and inserted into boreholes excavated at the gallery floor. In addition to the immersion tests, static leaching test with cubic type glass and ground water was also performed at the gallery. The samples of each test were collected in time intervals of 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, 3 years and 10 years and were subjected to weight loss measurement and several surface analyses. The results were as follows: (1)Weight losses of each sample were proportional to time intervals. This result is attributable to constant dissolved silica concentration in the ground water during tests. (2)The weight losses of disk type glass were slightly larger than those of cubic type glass. This result is attributable to elemental release from internal cracks of disk type glass, instead of effect of stainless steel on the glass dissolution. (3)The weight losses for the tests with clay were slightly smaller than those for tests without clay. This result is attributable to higher concentration of dissolved silica in pore water of clay.
10 mm (cubic type) and of 25 mm in diameter and 8 mm in thickness (disk type: The wall of sample was covered by stainless steel of 1 mm thick.) were used for the tests. Both type of samples with and without clay were put in Teflon vessels, which have small holes on the wall, and inserted into boreholes excavated at the gallery floor. In addition to the immersion tests, static leaching test with cubic type glass and ground water was also performed at the gallery. The samples of each test were collected in time intervals of 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, 3 years and 10 years and were subjected to weight loss measurement and several surface analyses. The results were as follows: (1)Weight losses of each sample were proportional to time intervals. This result is attributable to constant dissolved silica concentration in the ground water during tests. (2)The weight losses of disk type glass were slightly larger than those of cubic type glass. This result is attributable to elemental release from internal cracks of disk type glass, instead of effect of stainless steel on the glass dissolution. (3)The weight losses for the tests with clay were slightly smaller than those for tests without clay. This result is attributable to higher concentration of dissolved silica in pore water of clay.
Owada, Hitoshi*; Mihara, Morihiro; *; *
JNC TN8400 2000-027, 19 Pages, 2000/08
Bactch leaching experiments of granite with the artifitial cement leachate and the leachate of low-alkalinity-cement (LW) were carried out to evaluate the effect of the hiperalkaline plume on the environment of the high-level and TRU radioactive waste repository. Dissolution of Si and Al from feldspar included in the granite and precipitation of C-S-H were confirmed from the results of the leaching experiments with artifitial cement leachate. From this result it was found that the composition of sorrounding rock changed. It also suggested that the retardation factor of migration of radionuclides would change. On the contrary, only decrease of concentrations in Si, Al and Ca in the leachate was observed in the experiment with LW. This result might indicate that C-S-H and/or C-A-S-H precipitated as secondary minerals in the LW case. From these results, it was considered that the hiperalkaline plume from the cementitious leachate might caused the change of disposal conditions such as the change in distribution coefficients of rock by precipitation of the secondary mineral and the increase in hydraulic conductivity by the dissolution of rock. On the other hand, the influences of the LW would be comparatively small, because LW and granite might equilibrate in short time.
Saito, Junichi; Tachi, Yoshiaki; ; Kano, Shigeki
PNC TN9410 98-082, 60 Pages, 1998/08
Ceramics possessing high temperature strength are promising matelials for the structural application in severe environment. The development of ceramics has been carried out in order to use them in FBR environment such as liquid sodium. In particular, corrosion behavior of ceramics has been investigated to improve the corrosion resistance in liquid sodium. However, the corrosion mechanism of ceramics was not comprehended in detail even now. Because corrosion products which were deposited on the surface of test pieces a during corrosion test and played an important role in corrosion behavior were not detected distinctly after the corrosion test. In this study, an ion implantation technique was applied to understand the corrosion mechanism of ceramics in the stead of the conventional corrosion test. Sodium ions were implanted in ceramics (100keV, 1.9 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm ) and then heat treatment was performed at either 923K or 823K for 36ks in argon atmosphere. After that, products on the surface were analyzed using SEM and TEM observation and X-ray diffraction. Consequently, a kind of the corrosion product was not identified exactly, but the presence of corrosion products was confirmed on the surface. It caused by the amount of corrosion products was only a few. In future, it is necessary to carry systematically out the implantation and heat treatment under various conditions. Therefore, it seems that the beneficial information will be obtained to understand the corrosion mechanism of ceramics.
) and then heat treatment was performed at either 923K or 823K for 36ks in argon atmosphere. After that, products on the surface were analyzed using SEM and TEM observation and X-ray diffraction. Consequently, a kind of the corrosion product was not identified exactly, but the presence of corrosion products was confirmed on the surface. It caused by the amount of corrosion products was only a few. In future, it is necessary to carry systematically out the implantation and heat treatment under various conditions. Therefore, it seems that the beneficial information will be obtained to understand the corrosion mechanism of ceramics.
; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Kano, Shigeki; Yoshida, Eiichi
PNC TN9410 98-048, 56 Pages, 1998/03
Planar specimens of functionally gradient material (FGM) for thermal stress relaxation in fast reactor environment were formed and evaluated. FGMs of Al O
O -SUS316L system and Y
-SUS316L system and Y O
O -SUS316L system were deposited on SUS316L substrates by low pressure plasma spraying. The deposited coatings with 6 layers in which the ratio of ceramics/SUS316FR changes from 0 to 100% by 20% were successfully formed. Cross-sectional observation of the coatings showed no cracks and the hardness in the coating increased continuously from the substrate to the surface. From the results of X-ray diffraction, there were no changes in the structure of SUS316L and Y
-SUS316L system were deposited on SUS316L substrates by low pressure plasma spraying. The deposited coatings with 6 layers in which the ratio of ceramics/SUS316FR changes from 0 to 100% by 20% were successfully formed. Cross-sectional observation of the coatings showed no cracks and the hardness in the coating increased continuously from the substrate to the surface. From the results of X-ray diffraction, there were no changes in the structure of SUS316L and Y O
O between the powder and the coating. On the contrary, in the case of Al
between the powder and the coating. On the contrary, in the case of Al O
O ,
,  - Al
- Al O
O phase was detected in the coating formed from
phase was detected in the coating formed from 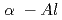 _
_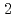
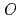 _
_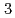 $ powder. The specimens were exposed in liquid sodium at 823K or 923K for 3.6Ms(1000h). The coatings were damaged with many cracks in liquid sodium. It was revealed that the bonding strength between the sprayed particles were not sufficient. To improve the stability in liquid sodium, another specimens were formed with changing the chamber pressure during deposition. From the microstructural inspections of the specimens, the coating formed at higher chamber pressure showed less porosity.
$ powder. The specimens were exposed in liquid sodium at 823K or 923K for 3.6Ms(1000h). The coatings were damaged with many cracks in liquid sodium. It was revealed that the bonding strength between the sprayed particles were not sufficient. To improve the stability in liquid sodium, another specimens were formed with changing the chamber pressure during deposition. From the microstructural inspections of the specimens, the coating formed at higher chamber pressure showed less porosity.
; Kano, Shigeki; ; Tachi, Yoshiaki; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Yoshida, Eiichi
PNC TN9410 98-021, 68 Pages, 1998/02
Engineering ceramics have excellent properties such as high strength, high hardness and high heat resistance compared with metallic matelials. To apply the ceramic in fast reactor environment, it is necessary to evaluate the sodium compatibility and the influence of sodium on the mechanical properties of ceramics. In this study, the influence of high temperature sodium on the mechanical properties of sintered ceramics of conventional and high purity Al O
O , SiC, SiAlON, AlN and unidirectional solidified ceramics of Al
, SiC, SiAlON, AlN and unidirectional solidified ceramics of Al O
O /YAG eutectic composite were investigated by means of flexure tests. Test specimens were exposed in liquid sodium at 823K and 923K for 3.6Ms. There were no changes in the flexural strength of the conventional and high purity Al
/YAG eutectic composite were investigated by means of flexure tests. Test specimens were exposed in liquid sodium at 823K and 923K for 3.6Ms. There were no changes in the flexural strength of the conventional and high purity Al O
O , AlN and Al
, AlN and Al O
O /YAG eutectic composite after the sodium exposure at 823K. On the contrary, the decrease in the flexural strength was observed in SiC and SiAlON. After the sodium exposure at 923K, there were also no changes in the flexural strength of AlN and Al
/YAG eutectic composite after the sodium exposure at 823K. On the contrary, the decrease in the flexural strength was observed in SiC and SiAlON. After the sodium exposure at 923K, there were also no changes in the flexural strength of AlN and Al O
O /YAG eutectic composite. In the conventional and high purity Al
/YAG eutectic composite. In the conventional and high purity Al O
O and SiC, the flexural strength decreased and signs of grain boundary corrosion were detected by surface observation. The flexural strength of SiAlON after the sodium exposure at 923K increased instead of severe corrosion. In the specimens those showed no changes in the flexural strength, further exposure in sodium is needed to verify whether the mechanical properties degrade or not. For SiAlON, it is necessary to clarify the reason for the increased strength after the sodium exposure at 923K.
and SiC, the flexural strength decreased and signs of grain boundary corrosion were detected by surface observation. The flexural strength of SiAlON after the sodium exposure at 923K increased instead of severe corrosion. In the specimens those showed no changes in the flexural strength, further exposure in sodium is needed to verify whether the mechanical properties degrade or not. For SiAlON, it is necessary to clarify the reason for the increased strength after the sodium exposure at 923K.
Iriya, Keishiro*; *
PNC TJ1201 94-004, 335 Pages, 1994/03
no abstracts in English
Morinaga, Masahiko*; Inoue, Satoshi*; Saito, Junichi*; *; *; Kano, Shigeki; Tachi, Yoshiaki
PNC TY9623 93-005, 134 Pages, 1993/03
None
Kajima Corporation*; Obayashi Corporation*; Shimizu Corporation*; Taisei Corporation*
PNC TJ1449 92-005, 351 Pages, 1992/02
None
*; Wada, Ryutaro*; *; Fujiwara, Kazuo*; *; Tomari, Haruo*
PNC TJ1058 91-012, 335 Pages, 1991/09
None
*; Morinaga, Masahiko*; Saito, Junichi*; *; *
PNC TJ9623 92-001, 81 Pages, 1991/07
[PURPOSE] For structural materials serviced in the Li environments, both Nb-based and Mo-based alloys are selected as the candidate materials. In this study, a simple method was proposed for evaluating the high temperature strength of these alloys. Also, the corrosion resistance in liquid metals was investigated in order to get fundamental information for the design and development of high performance alloys. [EXPERIMENTAL AND CALCULATING METHODS] With a variety of ternary alloys high temperature micro-hardness was measured systematically. The results were analyzed by referring to the relationship between the hardness and the tensile strength reported in previous publications. Also, some alloys designed last year were exposed to the liquid Na at 650  C, and the attendant changes were examined with respect to the weight, microstructure and local composition of alloys. Some of the results were understood in terms of the free energy for the oxide formation of Na and other elements in alloys. Another effort to understand the corrosion properties was made by the molecular orbital calculation of the electronic states of various elements in liquid Li, K and Na. [RESULTS] The high temperature tensile strength of both the alloys was found to be predictable by using a linear relationship between the hardness and the tensile strength of room temperature to 1200
C, and the attendant changes were examined with respect to the weight, microstructure and local composition of alloys. Some of the results were understood in terms of the free energy for the oxide formation of Na and other elements in alloys. Another effort to understand the corrosion properties was made by the molecular orbital calculation of the electronic states of various elements in liquid Li, K and Na. [RESULTS] The high temperature tensile strength of both the alloys was found to be predictable by using a linear relationship between the hardness and the tensile strength of room temperature to 1200  C. The corrosion resistance was much poorer in the Nb-based alloys than in the Mo-based alloys. This is partially due to the enhancement of corrosion by the preferred oxidation of Nb and Ta in the Nb-based alloys, whereas no such oxidation took place in the Mo-based alloys. In addition, it was found from the molecular orbital calculation that Li is the liquid metal of more strongly-bonded with every alloying element, compared to K and Na liquid metals. Futhermore, it was shown that the hardness of each alloy correlated well with the atomic-size difference and also the young's modulus difference ...
C. The corrosion resistance was much poorer in the Nb-based alloys than in the Mo-based alloys. This is partially due to the enhancement of corrosion by the preferred oxidation of Nb and Ta in the Nb-based alloys, whereas no such oxidation took place in the Mo-based alloys. In addition, it was found from the molecular orbital calculation that Li is the liquid metal of more strongly-bonded with every alloying element, compared to K and Na liquid metals. Futhermore, it was shown that the hardness of each alloy correlated well with the atomic-size difference and also the young's modulus difference ...
*; *; Koakutsu, Toru; *; *
PNC TN9410 89-148, 158 Pages, 1989/10
For the purpose of the verification of the evaluation method on the sodium environmental effect on the mechanical properties of the structural materials used for the prototype LMFBR "MONJU" and the rationalization of the evaluation method for large scale LMFBRs, SUS 304 and 316 austenitic stainless steels and 2.25Cr-1Mo steel (NT) were carried out. Test specimens were exposed to a sodium loop for 10,000 hours at 400  600
600 C simulating the primary and secondary coolant systems of the prototype LMFBR "MONJU". After the exposure, fatigue tests were performed in sodium environment. Fatigue tests were also performed on the thermal aged material for 10.000 hours in inert gas. The results obtaind were as follows. (1)The difference between the fatigue lives of sodium exposed materials and thermal aged materials was very small for both kinds of steels and these lives were almost the same as these of as - received materials. (2)Caburization was recognized on the surface of SUS 304 and SUS 316 austenitic stainless steels in the cage tested in sodium after sodium exposed. In the case of 2.25Cr-1Mo steel (NT), some decarburization was observed at 500
C simulating the primary and secondary coolant systems of the prototype LMFBR "MONJU". After the exposure, fatigue tests were performed in sodium environment. Fatigue tests were also performed on the thermal aged material for 10.000 hours in inert gas. The results obtaind were as follows. (1)The difference between the fatigue lives of sodium exposed materials and thermal aged materials was very small for both kinds of steels and these lives were almost the same as these of as - received materials. (2)Caburization was recognized on the surface of SUS 304 and SUS 316 austenitic stainless steels in the cage tested in sodium after sodium exposed. In the case of 2.25Cr-1Mo steel (NT), some decarburization was observed at 500  C. (3)The fatigue lives didnot depend on the exposure history such as sodium exposed materials and thermal aged materials for 10,000 hours. The carburization and decarburization effects were very small on fatigue life. The fatigue lives were affected by the environment in which fatigue tests are conducted.
C. (3)The fatigue lives didnot depend on the exposure history such as sodium exposed materials and thermal aged materials for 10,000 hours. The carburization and decarburization effects were very small on fatigue life. The fatigue lives were affected by the environment in which fatigue tests are conducted.
Kawato, Takaya*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Takeshi*; Minato, Daisuke*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Mihara, Morihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*
no journal, ,
Since fuel debris recovered from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant may be directly disposed of in deep geological strata, knowledge of dissolution reactions of fuel debris in water and chemical states of dissolved nuclides is essential for safety assessment of disposals. The chemical composition and physical properties of fuel debris depend on the atmosphere and temperature, but the formation of FeUO has been suggested at conditions under which air enters the reactor from outside. Uranium in FeUO
has been suggested at conditions under which air enters the reactor from outside. Uranium in FeUO is reported to be pentavalent, but no dissolution reaction in water has been investigated. In this study, FeUO
is reported to be pentavalent, but no dissolution reaction in water has been investigated. In this study, FeUO was synthesized by heating at a predetermined temperature and oxygen pressure, immersed in nitric acid to remove unreacted uranium oxides, and then immersed in a solution of pH2-8. After the prescribed period, pH and Eh values were measured, and dissolved iron and uranium concentrations were measured by ICP-MS. X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to evaluate the solid state before and after immersion. From these results, it was interpreted that the dissolution of FeUO
was synthesized by heating at a predetermined temperature and oxygen pressure, immersed in nitric acid to remove unreacted uranium oxides, and then immersed in a solution of pH2-8. After the prescribed period, pH and Eh values were measured, and dissolved iron and uranium concentrations were measured by ICP-MS. X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to evaluate the solid state before and after immersion. From these results, it was interpreted that the dissolution of FeUO was accompanied by a redox reaction between Fe(III)/Fe(II) and U(V)/U(VI) during dissolution.
was accompanied by a redox reaction between Fe(III)/Fe(II) and U(V)/U(VI) during dissolution.